Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on 1st Feb presented Union Budget 2024 in Parliament. This was an interim budget as it came just ahead of the Lok Sabha Elections.
This was Nirmala Sitharaman's sixth Union Budget. The full-fledged budget will be presented by the new government that comes to power after the elections.
The interim budget – a short-term financial plan – seeks Parliament nod for a grant in advance to meet the government's essential expenditure for the first four months of the new financial year.
The Budget Session of Parliament began yesterday with President Droupadi Murmu addressing the joint meeting of both Rajyya Sabha and Lok Sabha. The session will conclude on February 9.
Finance Minister announcements ranged from railways, tourism, healthcare technology, aviation, green energy, aquaculture, housing, and more. With regards to taxation, no changes were announced to the tax structure of direct and indirect taxes, and import duties. Meanwhile, startups and investments made by sovereign wealth or pension funds were given an extended tax exemption till March 31, 2025.
Briefcase to 'Bahi Khata' to make-in-India tablet: Evolution of Union Budget
-Nirmala Sitharaman shifted from a traditional briefcase to a 'bahi khata' in 2019 and embraced a paperless format in 2021.
-The moves represented a rejection of colonial legacy and a commitment to 'Digital India'.
-This year too, the Finance Minister presented the Budget using a 'Made-in India' tablet.

HIGHLIGHTS :
- Rooftop solarization-1 crore households will be enabled to obtain up to 300 units of free electricity per month
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Grameen) close to achieving target of 3 crore houses, additional 2 crore targeted for next 5 years
- 30 crore Mudra Yojana loans given to women entrepreneurs
- No changes in direct / indirect tax rates
- Govt withdraws income tax demands up to ₹25,000 (till 2009-10) and ₹10,000 from FY2010-11 to 2014-15. This will benefit about one crore
- Fiscal deficit at 5.8% in FY24;
- FY25 projection at 5.1%
- Implementation of 3 major railway corridor programmes under PM Gati Shakti
- Special schemes for the development of Lakshadweep
- Roadmap for development of india in July 2024 Full Budget .

Budget2024 -Working to make India Viksit Bharat by 2047 , says Finance Minister.
We need to focus on four major groups (Four-Pillars of Vikshit Bharat)
• Gareeb (Poor)
• Mahilayein (Women)
• Yuva (Youth)
• Annadata (Farmers)
People-centric inclusive development plan, the Finance Minister announced-
-There will be substantive development of all forms of infrastructure – physical, digital and social.
-Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) will promote formalisation and financial inclusion.
-The government plans to deepen and widen the tax base via GST.
-Strengthened financial sector brought savings, credit and investment back on track.
-A robust gateway will be set up called GIFT IFSC will be set up for global capital and financial services for the economy.
-There will be proactive inflation management.
Four focus Areas :
1. Garib Kalyan, Desh ka Kalyan
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) has led to savings of Rs. 2.7 lakh crore.
- 25 crore people have moved out of multidimensional poverty.
- Credit assistance has been given to 78 lakh street vendors under PM-SVANidhi.
2. Empowering the Youth
- 1.4 crore youth have been trained under the Skill India Mission.
- Fostering entrepreneurial aspirations of youth – 43 crore loans have been sanctioned under the PM Mudra Yojana.
- A corpus of Rs.1 lakh crore to fund tech-savvy youth with a 50-year, interest-free loan at low or nil interest rates charge to provide financing/re-financing.
3. Welfare of Farmers (Annadata)
- There has been direct financial assistance provided to 11.8 crore farmers under PM-KISAN.
- Crop Insurance has been given to 4 crore farmers under PM Fasal Bima Yojana.
- There has been an integration of 1,361 mandis under eNAM, supporting trading volume of Rs.3 lakh crore.
4. Nari Shakti
- 30 crore Mudra Yojana loans have been disbursed to women entrepreneurs.
- There has been an increase in female enrollment in higher education by 28 per cent in the past 10 years.
- There is 43% of female enrolment in STEM(Science,Technology,Engineering and Mathematics) courses.
- One crore women are assisted by 83 lakh SHGs (Self Help Groups) to become Lakhpati Didis.
Strategy Shift for Amrit Kaal as Kartavya Kaal
1. Sustainable Development / Green Energy
The Finance Minister highlighted the need for sustainable development by committing to meet ‘Net Zero’ by 2070 under Amrit Kaal. In this regard, the FM proposed
- Viability gap funding for harnessing offshore wind energy for an initial capacity of one giga-watt.
- Setting up of coal gasification and liquefaction capacity of 100 MT by 2030.
- Phased mandatory blending of CNG, PNG, and compressed biogas for domestic purposes.
- Financial assistance for the procurement of biomass aggregation machinery.
- Further, there will be rooftop solarisation with one crore households enabled to obtain up to 300 units of free electricity per month.
- The government also plans to adopt e-buses for public transport and strengthen the e-vehicle ecosystem by supporting the manufacturing and charging of electric vehicles.
- A new scheme of biomanufacturing and bio-foundry will be launched to support environment-friendly alternatives.
- 1.3 crore LED street lights will be installed under the SNLP (Street Lighting National Programme) scheme.
- The Blue Economy 2.0 scheme will be launched to restore and adapt coastal aquaculture and mariculture.
2. Infrastructure and Investment
- The government plans to implement three major railway corridor programmes, being energy, minerals, and cement corridor, port connectivity corridor, and high traffic density corridor under the PM Gati Shakti. It will improve logistics efficiency and reduce costs.
- 40,000 normal rail bogies to be converted to Vande Bharat Standards.
- Foreign investment will be promoted via bilateral investment treaties to be negotiated.
- Expansion of existing airports and comprehensive development of new airports under the UDAN scheme.
- Urban transformation will occur under the Metro rail and NaMo Bharat projects.
3. Inclusive Development
The FM highlighted the need for inclusive development under Amrit Kaal, with an aspirational District Programme to assist states in faster development, including employment generation. In this regard,
Healthcare
- The government is actively encouraging cervical cancer vaccination for girls aged between 9-14 years.
- The Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 scheme would expedite the upgradation of Anganwadi centres to improve nutrition delivery, early childhood care and development.
- A U-WIN platform is to be rolled out for the immunisation efforts of Mission Indradhanush.
- Health coverage under the Ayushman Bharat scheme will be extended for all ASHA, Anganwadi workers, and helpers.
- A committee will be formed to study the issues faced in setting up more medical colleges in India.
Housing
- The Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (Grameen) is close to achieving the target of 3 crore houses, with an additional 2 crore targeted for the next 5 years.
- Housing for the middle class scheme to be launched to encourage the middle class to buy or build their own houses.
Tourism
- States will be encouraged to undertake the development of iconic tourist centres to attract business and promote opportunities for local entrepreneurship.
- Long-term interest-free loans are to be provided to states to encourage development.
- Projects for port connectivity, tourism infrastructure, and amenities will be taken up in islands, including Lakshadweep.
4. Agriculture and Food Processing
- The government is set to promote private and public investment in post-harvest activities.
- The application of Nano-DAP is to be expanded in all agro-climatic zones.
- Atmanirbhar Oilseeds Abhiyan strategy to be formulated to achieve atma nirbharta for oilseeds.
- A comprehensive programme for dairy development is to be formulated.
- The implementation of Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana will be stepped up to enhance aquaculture productivity, double exports, and generate more employment opportunities.
Tax Proposals
- The FM announced that the same tax rates will be retained in FY 2024-25 for direct and indirect taxes. There will be no tax liability for taxpayers with an income of up to Rs.7 lakh, under the new tax regime.
- The 22% tax rate for corporate taxes will apply for existing domestic companies and 15% for certain new manufacturing companies.
- The FM announced that direct tax collections have more than tripled over the last ten years, with the number of return filers at 2.4 times.
- On the other hand, the average processing time of tax returns has reduced from 93 days in 2013-14 to 10 days in 2023-24.
- The FM has proposed an extension in the time limit for certain tax benefits for start-ups and investments made by sovereign wealth funds/pension funds, and a tax exemption for specific IFSC units that expires on 31st March 2024. The same has been extended up to 31st March 2025.
Goods and Services Tax
GST has Enabled ONE NATION , ONE MARKET, ONE TAX , SAYS FM
- The FM announced that the average monthly gross GST collection has doubled to Rs.1.66 lakh crore in FY24.
- There has been an increase in the tax buoyancy of state revenue from 0.72 in 2012-16 to 1.22 in the post-GST period of 2017-23.
- The FM announced that the same customs rates, including import duties, will be retained in FY 2024-25.
GST Collection
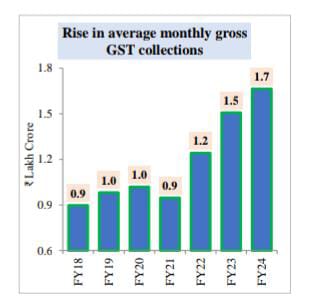
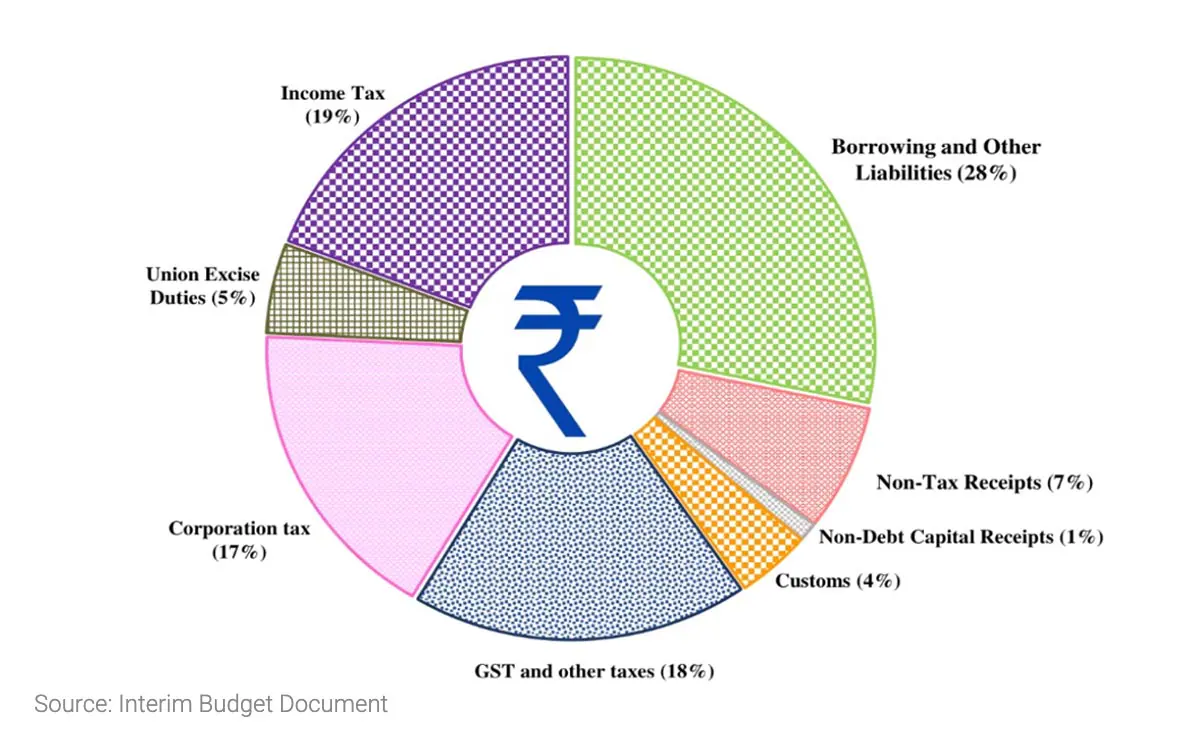
Revenue Streams of Government :
Rupee Comes From
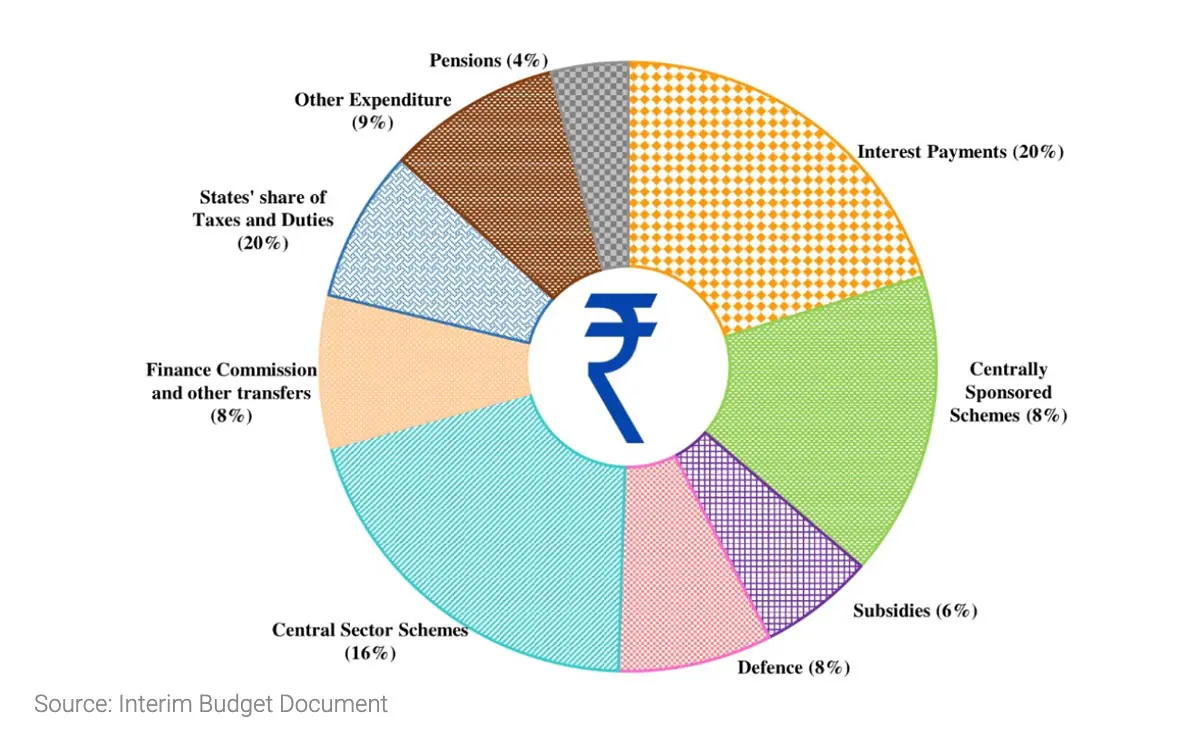
Government Spending
Rupee goes to
Ministry – Wise Allocation
|
Ministry
|
INR(in lakh crore)
|
|
Ministry of defence
|
6.2
|
|
Ministry of Road Transport And Highyways
|
2.78
|
|
Ministry of Railways
|
2.55
|
|
Ministry of Consumers Affairs ,Food and Public Distribution
|
2.13
|
|
Ministry of Home Affairs
|
2.03
|
|
Ministry of Rural Development
|
1.77
|
|
Ministry of Chemical And Fertilisers
|
1.68
|
|
Ministry of Communication
|
1.37
|
|
Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare
|
1.27
|
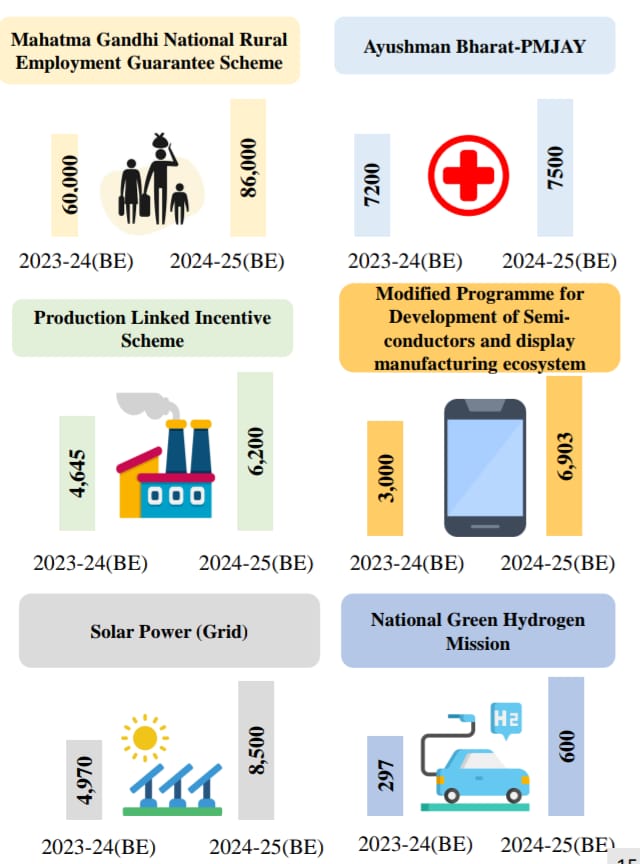
Allocation to Major Schemes (INR in crore)
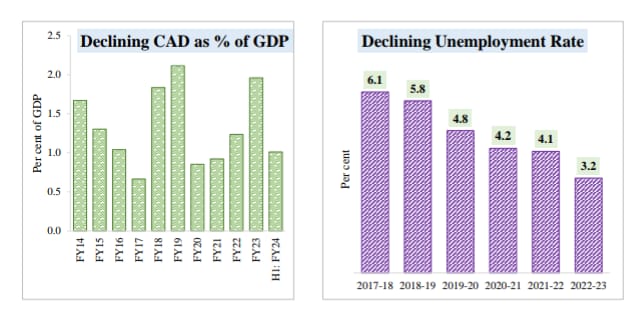
Performance of Indian Economy
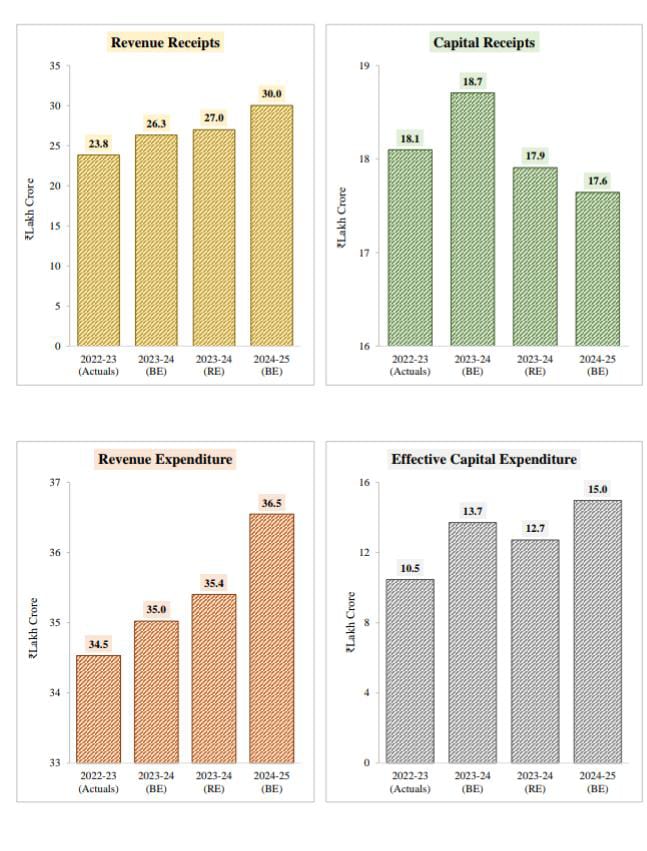
Budget at a Glance
MAJOR ANNOUNCEMENTS
– CAPEX Outlay increased by 11% to 11 lakh crore ~ 3.4% of GDP
– 1 Lakh Cr to be allocated for research and development of defence technologies
-Fiscal Deficit(Fiscal Deficit is the difference between the total revenue & total expenditure of a govt in a financial year) FY24-5.8%. Expected Fiscal deficit for FY25-5.1% of GDP, beating all market estimates
– 75,000 CR interest free 50 year loan is proposed to support milestone-linked reforms by the State Governments.
In conclusion, the Interim Budget 2024-25 reflects the government's continued focus on inclusive growth, economic stability, strategic global positioning, sector-specific developments, environmental sustainability, and tax reforms, with an overarching vision towards a developed India by 2047.

