Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on 1st February presented the annual budget of the country. The Budget announcement brought a series of key announcements for the nation’s middle class.
“The new structure will substantially reduce access of the middle class and leave more money in their hands, boosting household consumption, savings and investment in the new tax regime,” said FM Sitharaman.
This Union Budget will be 2nd full-fledged budget in Modi 3.0 and her eighth budget in overall parliament. She has presented six full- fledged and two interim budget as Finance Minister of the Country.
The first part of the Parliament’s Budget session began on January 31 and will end on February 13, 2025. The second part will commence on March 10 and conclude on April 4, 2025.
Budget 2025 is expected to provide incentives to key areas, including measures to boost the agricultural sector, employment schemes, tax benefits, schemes for MSMEs, and infrastructure development measures. The Budget 2025-26 focuses on critical issues such as tax policies, expenditure priorities, and subsidies. One of the key expectations is a revision in the tax slabs, mainly aimed at providing relief to the middle class.
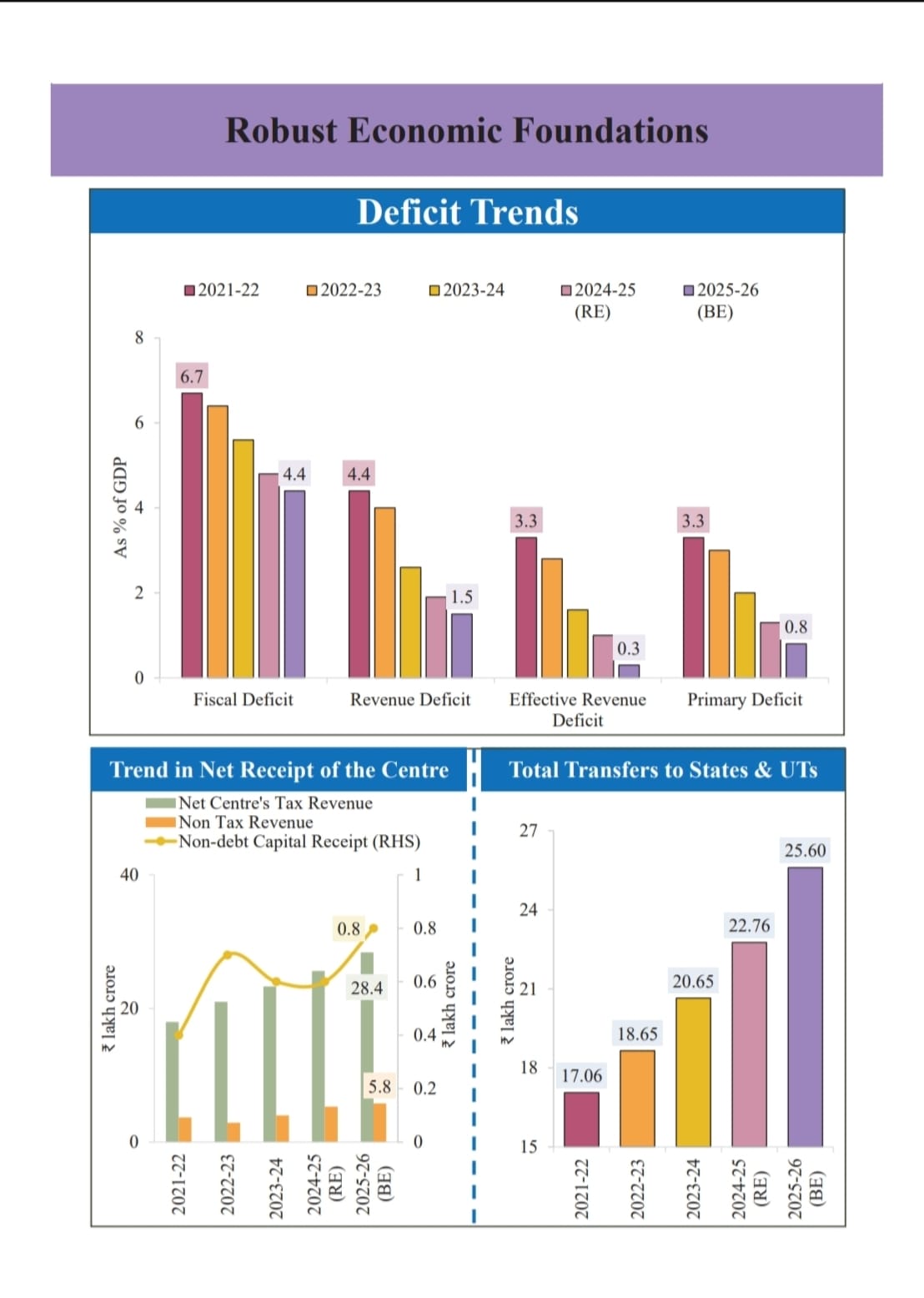
Budget Estimates for 2025-26
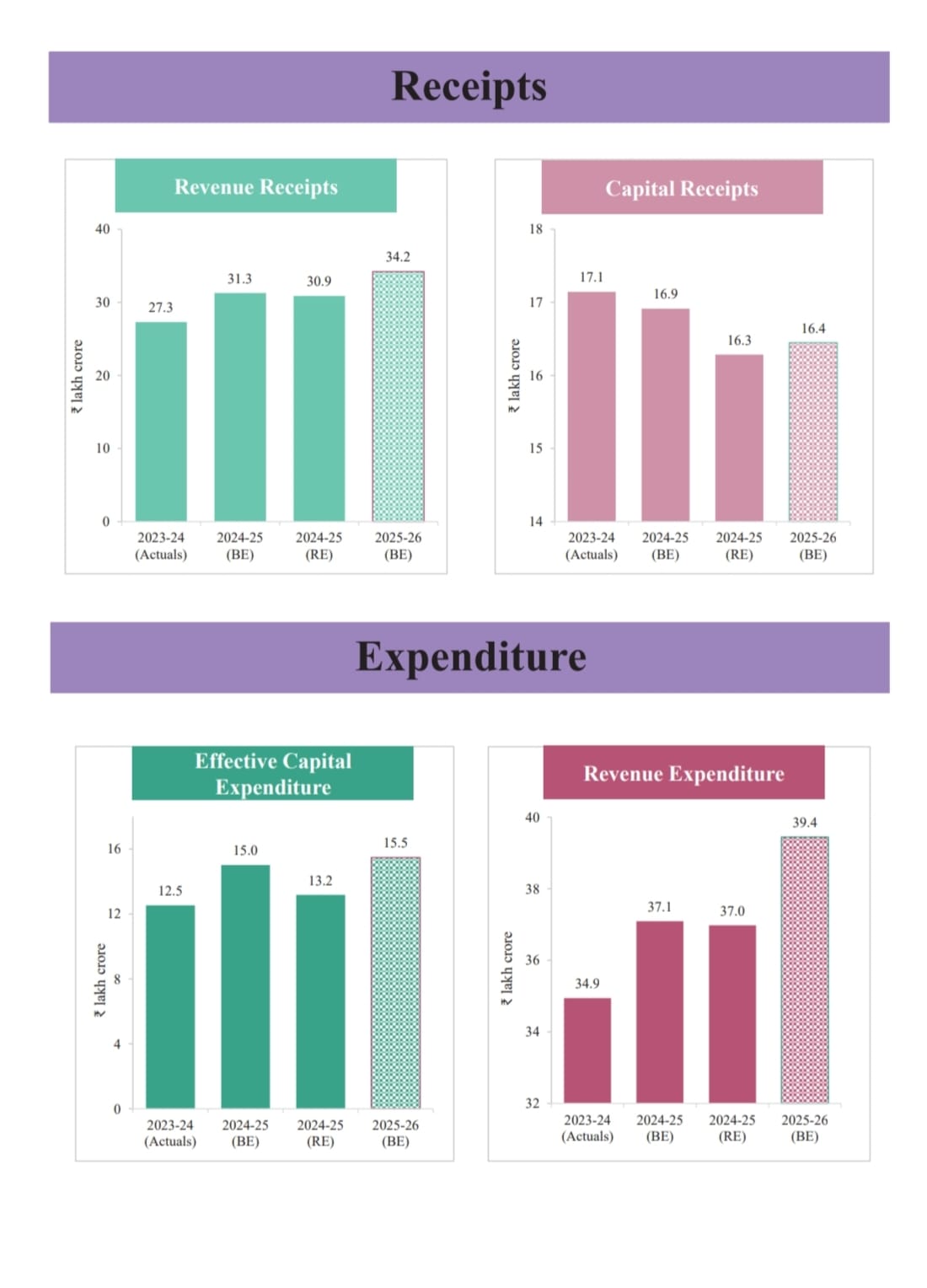
– Total receipts other than borrowing: ₹34.96 lakh crore
– Total expenditure: ₹50.65 lakh crore
– Fiscal Deficit: 4.4% of GDP. To finance the fiscal deficit, the net market borrowings from dated securities are estimated at ₹11.4 lakh crore
Key highlights of the Union Budget:
1) Medical education and health infrastructure which includes medical seats boost of 10,000 seats and cancer care expansion which means 200 cancer centres will be established in 2025-28.
2) MSMEs, start-ups and Artificial Intelligence which includes higher credit guarantees for small businesses, 10,000 crore rupees funds for start-ups and 500 crore rupees for AI infrastructure.
3) Green Energy and Sustainability includes investment in solar, nuclear & hydropower, climate finance taxonomy and Electric- Vehicle boost.
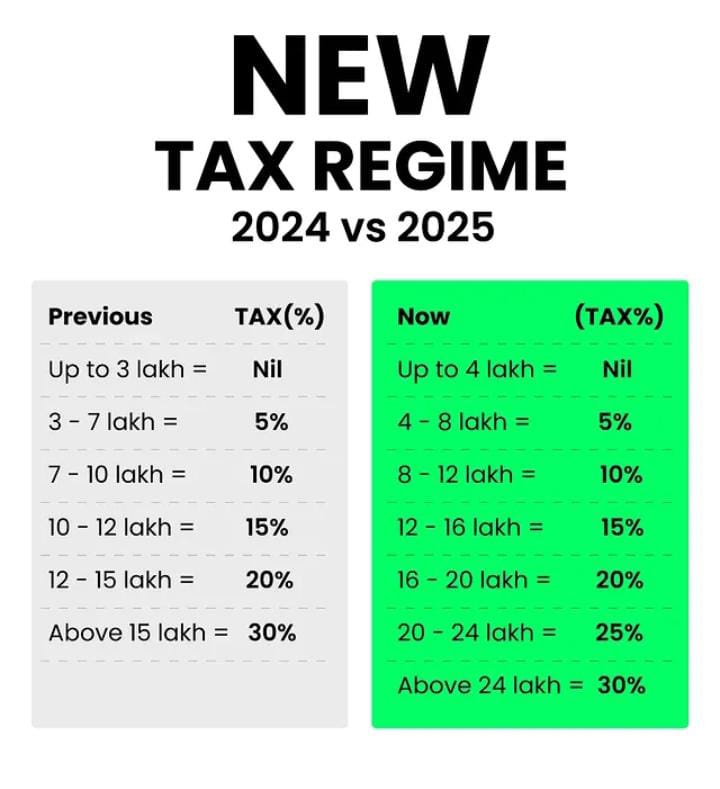
4) Tax & Middle-Class relief includes ‘Nil tax’ slab up to 12 lakh rupees , new income tax bill in the next week and tax filer update which is out of the 7.5 crore returns filed in FY 23-24, approximately 6.5 crore had income less than 12 lakh, meaning 87% of tax filers will have Zero tax liability this year.
5) Infrastructure & Transport includes state loan scheme of 1.5 trillion rupees in interest free loans, maritime development funds and new greenfield Airports in bihar.
6) Economy & Fiscal Deficit which includes:
– Fiscal deficit target of FY25 at 4.8% of GDP, 4.4% for FY26
– India’s GDP expected to grow at 6.5%
Four Engines of Development follows: Development measures focusing on Garib, Youth, Annadata and Nari.
1) Agriculture: The Pradhan Mantri Dhan Dhanya Krishi Yojana and the developing agri-districts program will encompass 100 districts.
• A national mission focused on high-yielding seeds will be implemented.
• A comprehensive program addressing vegetable and fruit production will be launched in collaboration with state governments.
A Makhana Board will be established in Bihar
.• Given India’s position as the second-largest global producer of fishery products, the government will establish a supportive framework for the sustainable development of fisheries within India’s exclusive economic zone.
• A dedicated mission for cotton productivity will significantly enhance cotton farming practices.
• Kisan Credit Cards, providing short-term loans to 77 million farmers, fishermen, and dairy farmers, will see their credit limits increased from ₹300,000 to ₹500,000.
• To achieve self-reliance (Atmanirbharta) in urea production, a new plant with an annual capacity of 1.27 million metric tonnes will be constructed in Assam.
• Leveraging its network of 150,000 rural post offices and the India Post Payments Bank, India Post will be strategically repositioned to stimulate rural economic growth and will be developed into a major public sector logistics organization to meet increasing demands.
2) MSME:
Credit Cards for Micro Enterprises: Customised Credit Cards with a five lakh rupees limit for micro enterprises registered on Udyam portal. In the first year, 10 lakh such cards will be issued.
Scheme for first time Entrepreneurs: for 5 lakh first- time entrepreneurs, including women, Scheduled castes, Scheduled tribes, a new scheme, to be launched to provide term loans up to 2 crore rupees during the next 5 years.
Manufacturing mission focuses on ease and cost of doing business, a vibrant and dynamic MSME sector, availability of technology and clean tech manufacturing for climate-friendly development.
3) Investment: The Minister of Finance, Ms. Sitharaman, identifies investment as the third engine of growth, encompassing investments in human capital, economic infrastructure, and innovation.
Investing in Human Capital:
The Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 initiatives provide nutritional support to over 80 million children, 10 million pregnant women and mothers, and 2 million adolescent girls. The program’s funding will be increased.
Fifty thousand Atal Tinkering Labs will be established in government schools over the next five years.
Broadband connectivity will be extended to all government secondary schools and primary centres in rural areas.
A Bharatiya Bhasha Pustak scheme will be implemented to provide Indian language books for schools and higher education institutions.
Five national centres of excellence for skill development will be established, leveraging global expertise and partnerships, building upon the announcements made in the July 2024 budget.
The capacity of the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) will be expanded. Enrolment in the 23 IITs has doubled from 65,000 to 135,000 students over the past decade. Additional infrastructure will be developed at the five IITs established after 2014, and IIT Patna will also undergo expansion.
4) Export:
Export Promotion Mission: with sectoral and ministerial targets to facilitate easy access to export credit, cross-border factoring support, and support to MSMEs to tackle non-tariff measures in overseas markets.
Bharat Trade Net: A digital public infrastructure for international trade will be set-up as a unified platform for trade documentation and financing solutions. Support for integration with Globally Supply Chains.
National Framework for GCC: As guidance to states for promoting Global Capability Centres in emerging tier 2 cities.
Warehousing facility for air cargo: To facilitate upgradation of infrastructure and warehousing for air cargo including high value perishable horticulture produce.
Major points:
An enhanced UDAAN regional connectivity scheme will be implemented:
• The UDAAN scheme has facilitated air travel for 15 million middle-class citizens.
• A revised UDAAN scheme will expand regional connectivity to 120 new destinations, serving 40 million passengers over the next decade. This initiative will also support the development of helipads and smaller airports in mountainous and underserved regions.
• New airport construction will be supported in Bihar to meet future demand, supplementing the expansion of Patna Airport.
• The Western Kosi Canal project in Mithilanchal will receive financial backing, benefiting a substantial number of Bihar’s farmers.
Nuclear Energy Initiative:
• Achieving a minimum of 100 GW of nuclear energy capacity by 2047 is critical to our energy transition strategy.
• To foster robust private sector engagement, revisions to the Atomic Energy Act and the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act will be implemented.
• A dedicated ₹200 crore Nuclear Energy Research and Development Mission will be established to advance small modular reactor technology. The operational deployment of at least five domestically developed small modular reactors is targeted for 2033.
Revision of tax slabs under new tax regime:
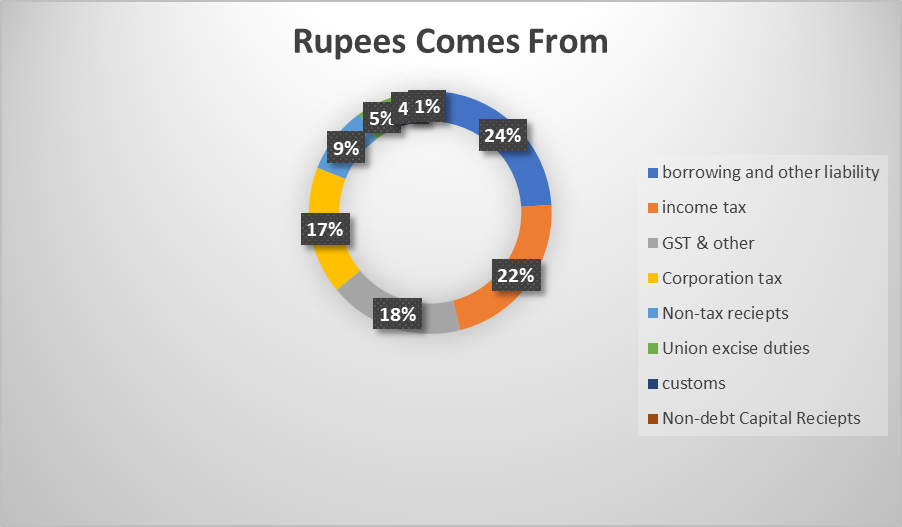
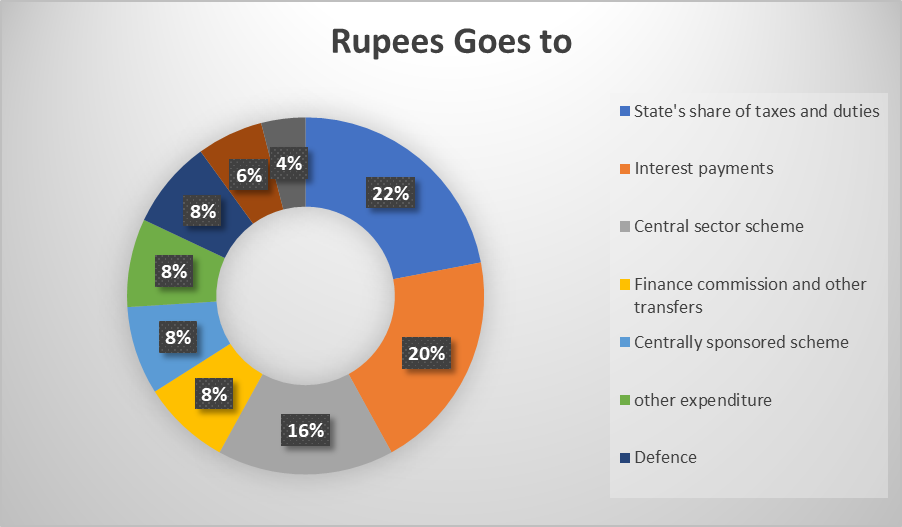
Budget at a glance:
Ministry wise allocation: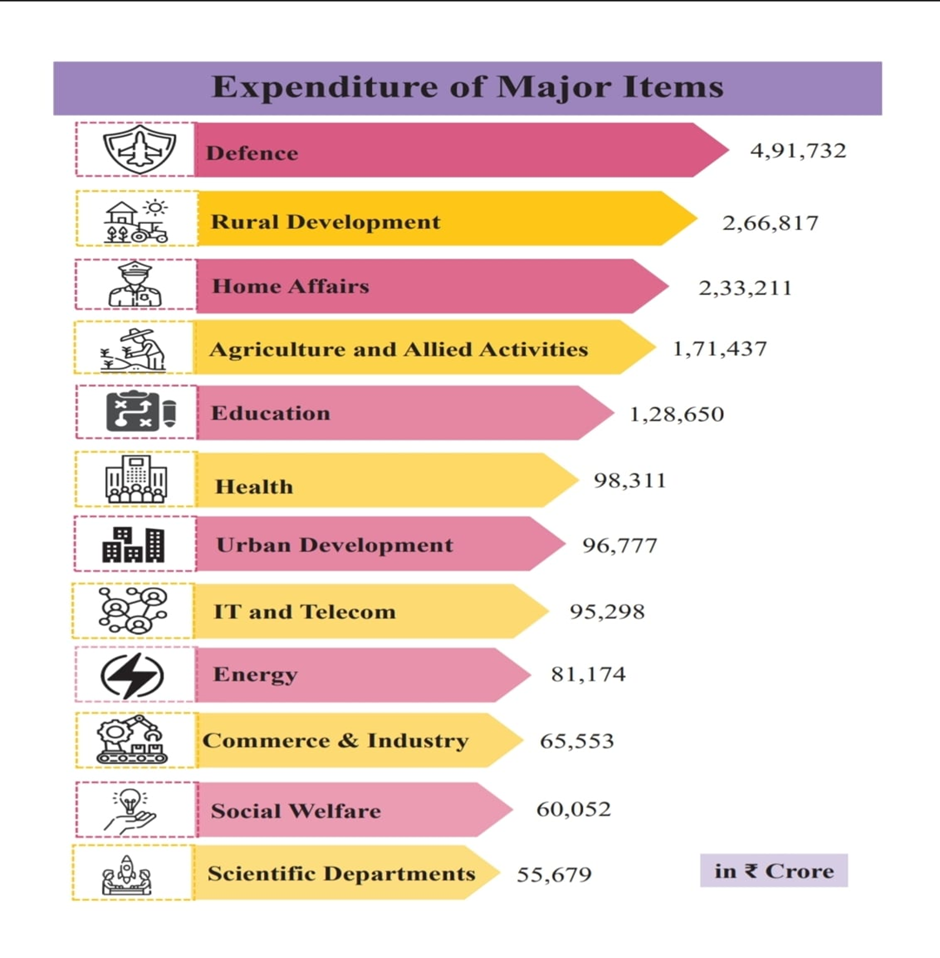
In conclusion of the 2025 budget will aim to strike a balance between sustaining vital government functions, promoting economic growth, and managing the national debt. The budget will reflect the administration’s priorities for the year ahead, responding to both domestic and global economic conditions.

